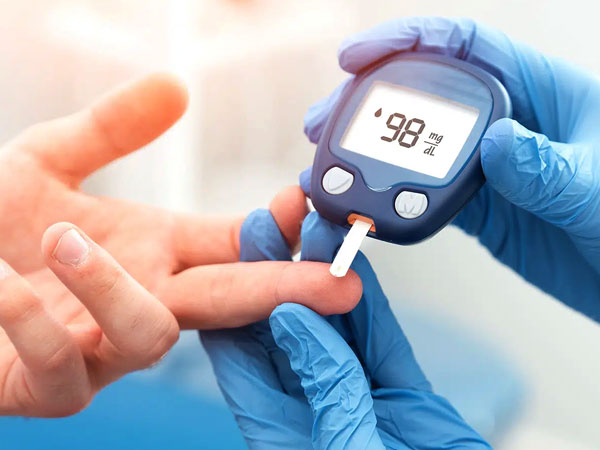


Diabetes
Diabetes happens when your body isn't able to take up sugar (glucose) into its cells and use it for energy. This results in a build up of extra sugar in your bloodstream.
Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to serious consequences, causing damage to a wide range of your body's organs and tissues – including your heart, kidneys, eyes and nerves.
What are the different types of diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. In this case, the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Up to 10% of people who have diabetes have Type 1. It’s usually diagnosed in children and young adults (but can develop at any age). It was once better known as “juvenile” diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. This is why it is also called insulin-dependent diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or your body’s cells don’t respond normally to the insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes. Up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older people. Other common names for Type 2 include adult-onset diabetes and insulin-resistant diabetes. Your parents or grandparents may have called it “having a touch of sugar.”
Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, if you have gestational diabetes you're at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
What causes diabetes?
- Causes of Type 1 diabetes: This is an immune system disease. Your body attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in your pancreas. Without insulin to allow glucose to enter your cells, glucose builds up in your bloodstream. Genes may also play a role in some patients. Also, a virus may trigger the immune system attack.
- Cause of Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes: Your body’s cells don't allow insulin to work as it should to let glucose into its cells. Your body's cells have become resistant to insulin. Your pancreas can’t keep up and make enough insulin to overcome this resistance. Glucose levels rise in your bloodstream.
- Gestational diabetes: Hormones produced by the placenta during your pregnancy make your body’s cells more resistant to insulin. Your pancreas can’t make enough insulin to overcome this resistance. Too much glucose remains in your bloodstream.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
- Increased thirst
- Weak, tired feeling
- Blurred vision
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- Slow-healing sores or cuts
- Unplanned weight loss
- Frequent urination
- Frequent unexplained infections
- Dry mouth
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp